Doppler Effect (Sound)
Summary
- Drawing sound waves
- One dimensional technique
- Sound waves can be drawn as a pressure-time or pressure-distance graph.
- Sound waves are still longitudinal waves despite the fact that this technique makes them look like transverse waves.
- Two dimensional technique
- Sound waves can be drawn as wavefronts.
- Wavefronts are the locus of all points in space with the same phase.
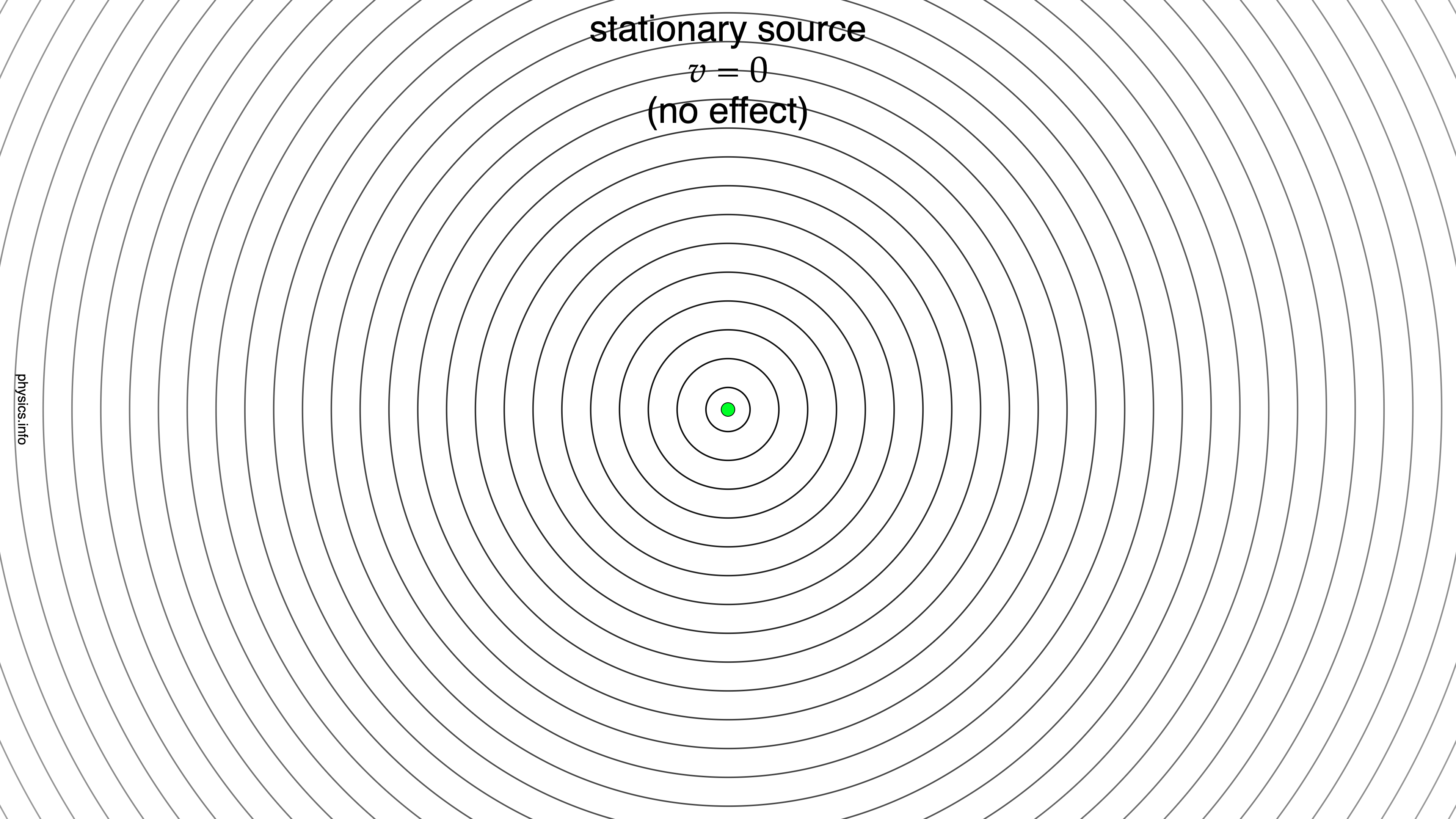
- The wavefronts from a stationary, point source of sound are concentric circles.
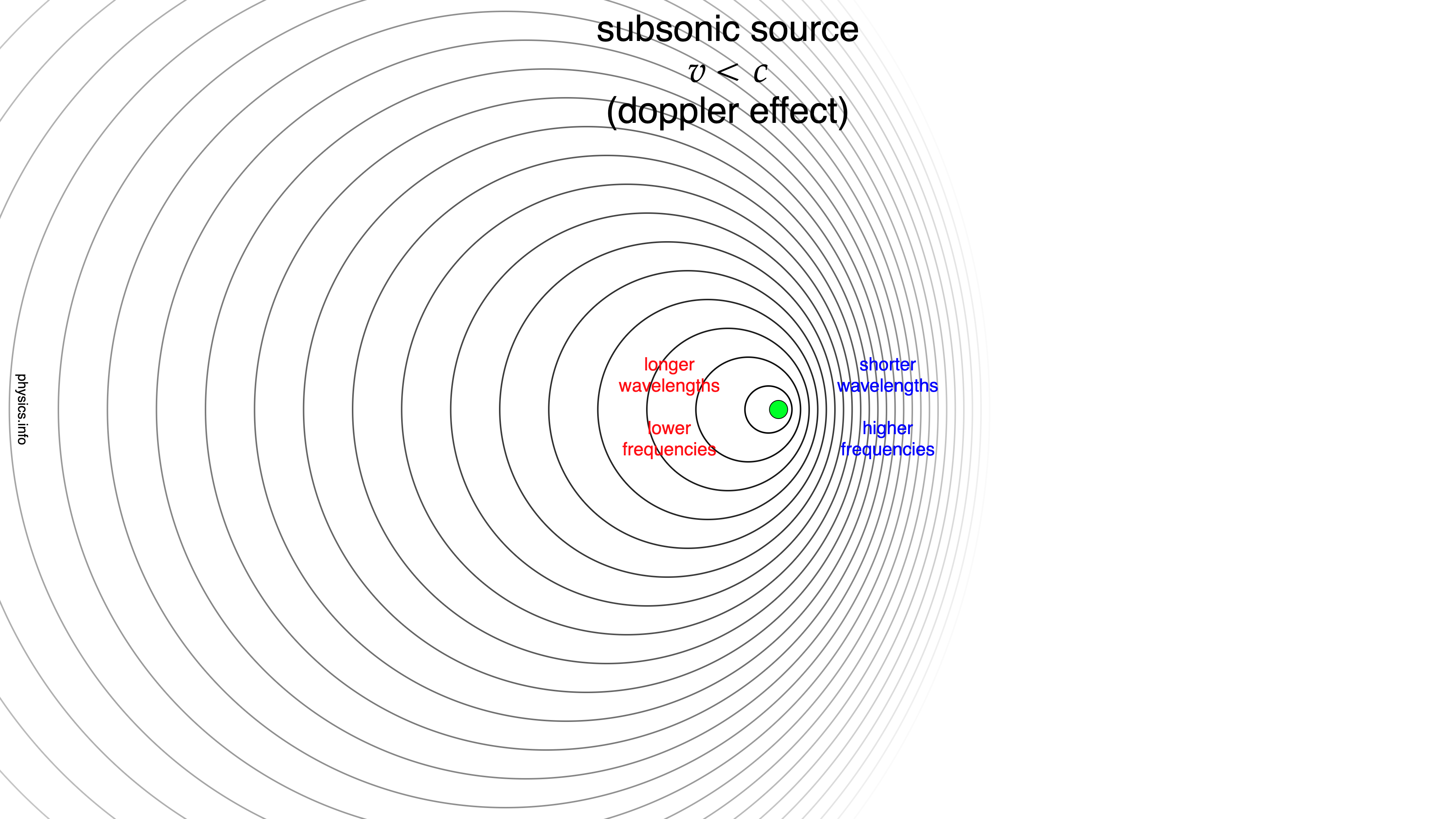
- The wavefronts from a moving, point source of sound are circles that are positioned closer together in front of the source and farther apart behind the source.
- One dimensional technique
- The Doppler effect…
- is the apparent change in the frequency of a wave caused by relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer.
- applies to all types of waves.
- increases the frequency of a wave (raises the pitch of a sound wave) when the source moves toward the observer.
- decreases the frequency of a wave (lowers the pitch of a sound wave) when the source moves away from the observer.
- Animations
 |
 |
| speed regime |
relative speed |
mach number |
mach angle |
important concept |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stationary | 0 | 0 | wavefronts | |
| subsonic | <c | <1 | doppler effect | |
| transonic | ~c | ~1 | ~90° | sound barrier |
| supersonic | >c | >1 | <90° | shock wave |
| hypersonic | ≳5c | ≳5 | ≲10° | ? |